

| The World Factbook | ||


|
Malaysia |

|
|
| Introduction | Malaysia |
|
Background:
|
During the late 18th and 19th centuries, Great Britain established colonies and protectorates in the area of current Malaysia; these were occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1945. In 1948, the British-ruled territories on the Malay Peninsula formed the Federation of Malaya, which became independent in 1957. Malaysia was formed in 1963 when the former British colonies of Singapore and the East Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak on the northern coast of Borneo joined the Federation. The first several years of the country's history were marred by a Communist insurgency, Indonesian confrontation with Malaysia, Philippine claims to Sabah, and Singapore's secession from the Federation in 1965. During the 22-year term of Prime Minister MAHATHIR bin Mohamad (1981-2003), Malaysia was successful in diversifying its economy from dependence on exports of raw materials to expansion in manufacturing, services, and tourism. |
| Geography | Malaysia |
|
Location:
|
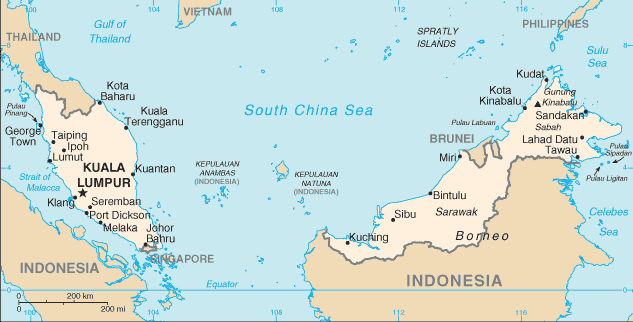
Southeastern Asia, peninsula bordering Thailand and northern one-third of the island of Borneo, bordering Indonesia, Brunei, and the South China Sea, south of Vietnam |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
2 30 N, 112 30 E |
|
Map references:
|
Southeast Asia |
|
Area:
|
total: 329,750 sq km
land: 328,550 sq km water: 1,200 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly larger than New Mexico |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 2,669 km
border countries: Brunei 381 km, Indonesia 1,782 km, Thailand 506 km |
|
Coastline:
|
4,675 km (Peninsular Malaysia 2,068 km, East Malaysia 2,607 km) |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation; specified boundary in the South China Sea |
|
Climate:
|
tropical; annual southwest (April to October) and northeast (October to February) monsoons |
|
Terrain:
|
coastal plains rising to hills and mountains |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point: Gunung Kinabalu 4,100 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
tin, petroleum, timber, copper, iron ore, natural gas, bauxite |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 5.46%
permanent crops: 17.54% other: 77% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
3,650 sq km (2003) |
|
Total renewable water resources:
|
580 cu km (1999) |
|
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
|
total: 9.02 cu km/yr (17%/21%/62%)
per capita: 356 cu m/yr (2000) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
flooding; landslides; forest fires |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
air pollution from industrial and vehicular emissions; water pollution from raw sewage; deforestation; smoke/haze from Indonesian forest fires |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
strategic location along Strait of Malacca and southern South China Sea |
| People | Malaysia |
|
Population:
|
25,715,819 (July 2009 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 31.4% (male 4,153,621/female 3,914,962)
15-64 years: 63.6% (male 8,210,373/female 8,143,043) 65 years and over: 5% (male 569,245/female 724,575) (2009 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 24.9 years
male: 24.3 years female: 25.6 years (2009 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
1.723% (2009 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
22.24 births/1,000 population (2009 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
5.02 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
NA
note: does not reflect net flow of an unknown number of illegal immigrants from other countries in the region (2009 est.) |
|
Urbanization:
|
urban population: 70% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization: 3% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.06 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/female total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2009 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 15.87 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 18.32 deaths/1,000 live births female: 13.24 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 73.29 years
male: 70.56 years female: 76.21 years (2009 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
2.95 children born/woman (2009 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.5% (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
80,000 (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
3,900 (2007 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria note: highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Malaysian(s)
adjective: Malaysian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Malay 50.4%, Chinese 23.7%, indigenous 11%, Indian 7.1%, others 7.8% (2004 est.) |
|
Religions:
|
Muslim 60.4%, Buddhist 19.2%, Christian 9.1%, Hindu 6.3%, Confucianism, Taoism, other traditional Chinese religions 2.6%, other or unknown 1.5%, none 0.8% (2000 census) |
|
Languages:
|
Bahasa Malaysia (official), English, Chinese (Cantonese, Mandarin, Hokkien, Hakka, Hainan, Foochow), Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Panjabi, Thai
note: in East Malaysia there are several indigenous languages; most widely spoken are Iban and Kadazan |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 88.7% male: 92% female: 85.4% (2000 census) |
|
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
|
total: 13 years
male: 12 years female: 13 years (2005) |
|
Education expenditures:
|
6.2% of GDP (2004) |
| Government | Malaysia |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Malaysia local long form: none local short form: Malaysia former: Federation of Malaya |
|
Government type:
|
constitutional monarchy
note: nominally headed by paramount ruler (commonly referred to as the King) and a bicameral Parliament consisting of a nonelected upper house and an elected lower house; all Peninsular Malaysian states have hereditary rulers (commonly referred to as sultans) except Melaka and Pulau Pinang (Penang); those two states along with Sabah and Sarawak in East Malaysia have governors appointed by government; powers of state governments are limited by federal constitution; under terms of federation, Sabah and Sarawak retain certain constitutional prerogatives (e.g., right to maintain their own immigration controls) |
|
Capital:
|
name: Kuala Lumpur
geographic coordinates: 3 10 N, 101 42 E time difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) note: Putrajaya is referred to as administrative center not capital; Parliament meets in Kuala Lumpur |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
13 states (negeri-negeri, singular - negeri) Johor, Kedah, Kelantan, Melaka, Negeri Sembilan, Pahang, Perak, Perlis, Pulau Pinang, Sabah, Sarawak, Selangor, and Terengganu; and one federal territory (wilayah persekutuan) with three components, city of Kuala Lumpur, Labuan, and Putrajaya |
|
Independence:
|
31 August 1957 (from the UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day/Malaysia Day, 31 August (1957) |
|
Constitution:
|
31 August 1957; amended many times, the latest in 2007 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on English common law; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court at request of supreme head of the federation; Islamic law is applied to Muslims in matters of family law and religion; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
21 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: King - Sultan MIZAN Zainal Abidin (since 13 December 2006); (the position of the king is primarily ceremonial)
head of government: Prime Minister Mohamed NAJIB bin Abdul Razak (since 3 April 2009); Deputy Prime Minister MUHYIDDIN bin Mohamed Yassin (since 9 April 2009) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime minister from among the members of Parliament with consent of the king elections: kings are elected by and from the hereditary rulers of nine of the states for five-year terms; election last held on 3 November 2006 (next to be held in 2011); prime minister designated from among the members of the House of Representatives; following legislative elections, the leader who commands the support of the majority of members in the House becomes prime minister (since independence this has been the leader of the UMNO party) election results: Sultan MIZAN Zainal Abidin elected king; in practice, selection is based on principle of rotation among rulers of states |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral Parliament or Parlimen consists of Senate or Dewan Negara (70 seats; 44 appointed by the king, 26 elected by 13 state legislatures; serve three-year terms with limit of two terms) and House of Representatives or Dewan Rakyat (222 seats; members elected by popular vote; serve up to five-year terms)
elections: House of Representatives - last held on 8 March 2008 (next to be held by June 2013) election results: House of Representatives - percent of vote - BN coalition 50.3%, opposition parties 46.8%, others 2.9%; seats - BN coalition 140, opposition parties 82 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Civil Courts include Federal Court, Court of Appeal, High Court of Malaya on peninsula Malaysia, and High Court of Sabah and Sarawak in states of Borneo (judges are appointed by the king on the advice of the prime minister); Sharia Courts include Sharia Appeal Court, Sharia High Court, and Sharia Subordinate Courts at state-level and deal with religious and family matters such as custody, divorce, and inheritance only for Muslims; decisions of Sharia courts cannot be appealed to civil courts |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
National Front (Barisan Nasional) or BN (ruling coalition) consists of the following parties: Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia Party or PGRM [KOH Tsu Koon]; Liberal Democratic Party (Parti Liberal Demokratik - Sabah) or LDP [LIEW Vui Keong]; Malaysian Chinese Association (Persatuan China Malaysia) or MCA [ONG Tee Keat]; Malaysian Indian Congress (Kongres India Malaysia) or MIC [S. Samy VELLU]; Parti Bersatu Rakyat Sabah or PBRS [Joseph KURUP]; Parti Bersatu Sabah or PBS [Joseph PAIRIN Kitingan]; Parti Pesaka Bumiputera Bersatu or PBB [Abdul TAIB Mahmud]; Parti Rakyat Sarawak or PRS [James MASING]; Sarawak United People's Party (Parti Bersatu Rakyat Sarawak) or SUPP [George CHAN Hong Nam]; United Malays National Organization or UMNO [NAJIB bin Abdul Razak]; United Pasokmomogun Kadazandusun Murut Organization (Pertubuhan Pasko Momogun Kadazan Dusun Bersatu) or UPKO [Bernard DOMPOK]; People's Progressive Party (Parti Progresif Penduduk Malaysia) or PPP [M.Kayveas]; Sarawak Progressive Democratic Party or SPDP [William MAWAN])
People's Alliance (Pakatan Rakyat) or PR (opposition coalition) consists of the following parties: Democratic Action Party (Parti Tindakan Demokratik) or DAP [KARPAL Singh]; Islamic Party of Malaysia (Parti Islam se Malaysia) or PAS [Abdul HADI Awang]; People's Justice Party (Parti Keadilan Rakyat) or PKR [WAN AZIZAH Wan Ismail]; Sarawak National Party or SNAP [Edwin DUNDANG] independent party: Sabah Progressive Party (Parti Progresif Saban) or SAPP [YONG Teck Lee] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Bar Council BERSIH (electoral reform coalition); PEMBELA (Muslim NGO coalition)
other: religious groups; women's groups; youth groups |
|
International organization participation:
|
ADB, APEC, APT, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, C, CP, EAS, FAO, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUC, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNMIT, UNWTO, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Ilango KARUPPANNAN
chancery: 3516 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 572-9700 FAX: [1] (202) 572-9882 consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New York |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador James R. KEITH
embassy: 376 Jalan Tun Razak, 50400 Kuala Lumpur mailing address: US Embassy Kuala Lumpur, APO AP 96535-8152 telephone: [60] (3) 2168-5000 FAX: [60] (3) 2142-2207 |
|
Flag description:
|
14 equal horizontal stripes of red (top) alternating with white (bottom); there is a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a yellow crescent and a yellow 14-pointed star; the crescent and the star are traditional symbols of Islam; the design was based on the flag of the US |
| Economy | Malaysia |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Malaysia, a middle-income country, has transformed itself since the 1970s from a producer of raw materials into an emerging multi-sector economy. Since coming to office in 2003, Prime Minister ABDULLAH has tried to move the economy farther up the value-added production chain by attracting investments in high technology industries, medical technology, and pharmaceuticals. The Government of Malaysia is continuing efforts to boost domestic demand to wean the economy off of its dependence on exports. Nevertheless, exports - particularly of electronics - remain a significant driver of the economy. As an oil and gas exporter, Malaysia has profited from higher world energy prices, although the rising cost of domestic gasoline and diesel fuel forced Kuala Lumpur to reduce government subsidies. Malaysia "unpegged" the ringgit from the US dollar in 2005 and the currency appreciated 6% per year against the dollar in 2006-08. Although this has helped to hold down the price of imports, inflationary pressures began to build in 2007 - in 2008 inflation stood at nearly 6%, year-over-year. The government presented its five-year national development agenda in April 2006 through the Ninth Malaysia Plan, a comprehensive blueprint for the allocation of the national budget from 2006-10. ABDULLAH has unveiled a series of ambitious development schemes for several regions that have had trouble attracting business investment. Real GDP growth has averaged about 6% per year under ABDULLAH, but regions outside of Kuala Lumpur and the manufacturing hub Penang have not fared as well. The central bank maintains healthy foreign exchange reserves and the regulatory regime has limited Malaysia's exposure to riskier financial instruments and the global financial crisis. Decreasing worldwide demand for consumer goods is expected to hurt economic growth, however. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$386.6 billion (2008 est.)
$367.8 billion (2007) $346 billion (2006) note: data are in 2008 US dollars |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$214.7 billion (2008 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
5.1% (2008 est.)
6.3% (2007 est.) 5.8% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$15,300 (2008 est.)
$14,800 (2007 est.) $14,200 (2006 est.) note: data are in 2008 US dollars |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 9.7%
industry: 44.6% services: 45.7% (2008 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
11.2 million (2008 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 13%
industry: 36% services: 51% (2005 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
3.7% (2008 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
5.1% (2002 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 1.4%
highest 10%: 39.2% (2003 est.) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
46.1 (2002) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
20.7% of GDP (2008 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $44.32 billion
expenditures: $55.01 billion (2008 est.) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
|
Public debt:
|
42.7% of GDP (2008 est.) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
5.8%
note: approximately 30% of goods are price-controlled (2008 est.) |
|
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
|
6.41% (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of money:
|
$49.41 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of quasi money:
|
$187.6 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of domestic credit:
|
$220 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|
$325.7 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
Peninsular Malaysia - rubber, palm oil, cocoa, rice; Sabah - subsistence crops, rubber, timber, coconuts, rice; Sarawak - rubber, pepper, timber |
|
Industries:
|
Peninsular Malaysia - rubber and oil palm processing and manufacturing, light manufacturing, electronics, tin mining and smelting, logging, timber processing; Sabah - logging, petroleum production; Sarawak - agriculture processing, petroleum production and refining, logging |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
4% (2008 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
102.9 billion kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
95.98 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
2.524 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 89.5%
hydro: 10.5% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
753,700 bbl/day (2008 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
501,100 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
546,300 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
308,500 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
4 billion bbl (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
64.5 billion cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
32.9 billion cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
31.6 billion cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
2.35 trillion cu m (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$27.44 billion (2008 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$195.7 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
electronic equipment, petroleum and liquefied natural gas, wood and wood products, palm oil, rubber, textiles, chemicals |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 15.6%, Singapore 14.6%, Japan 9.1%, China 8.8%, Thailand 5%, Hong Kong 4.6% (2007) |
|
Imports:
|
$156.2 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
electronics, machinery, petroleum products, plastics, vehicles, iron and steel products, chemicals |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Japan 13%, China 12.9%, Singapore 11.5%, US 10.8%, Taiwan 5.7%, Thailand 5.3%, South Korea 4.9%, Germany 4.6%, Indonesia 4.2% (2007) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$104.4 billion (31 December 2008 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$54.11 billion (31 December 2008 est.) |
|
Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:
|
$92.76 billion (2008 est.) |
|
Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:
|
$50.08 billion (2008 est.) |
|
Currency (code):
|
ringgit (MYR) |
|
Currency code:
|
MYR |
|
Exchange rates:
|
ringgits (MYR) per US dollar - 3.33 (2008 est.), 3.46 (2007), 3.6683 (2006), 3.8 (2005), 3.8 (2004) |
| Communications | Malaysia |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
4.35 million (2007) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
23.347 million (2007) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: modern system; international service excellent
domestic: good intercity service provided on Peninsular Malaysia mainly by microwave radio relay; adequate intercity microwave radio relay network between Sabah and Sarawak via Brunei; domestic satellite system with 2 earth stations; combined fixed-line and mobile cellular teledensity exceeds 110 per 100 persons international: country code - 60; landing point for several major international submarine cable networks that provide connectivity to Asia, Middle East, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean, 1 Pacific Ocean) (2007) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 35, FM 391, shortwave 15 (2001) |
|
Radios:
|
10.9 million (1999) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
88 (mainland Malaysia 51, Sabah 16, and Sarawak 21) (2006) |
|
Televisions:
|
10.8 million (1999) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.my |
|
Internet hosts:
|
377,716 (2008) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
7 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
15.868 million (2007) |
| Transportation | Malaysia |
|
Airports:
|
116 (2008) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 36
over 3,047 m: 5 2,438 to 3,047 m: 10 1,524 to 2,437 m: 7 914 to 1,523 m: 8 under 914 m: 6 (2008) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 80
914 to 1,523 m: 8 under 914 m: 72 (2008) |
|
Heliports:
|
2 (2007) |
|
Pipelines:
|
condensate 3 km; gas 1,965 km; oil 31 km; refined products 114 km (2008) |
|
Railways:
|
total: 1,890 km
standard gauge: 57 km 1.435-m gauge (57 km electrified) narrow gauge: 1,833 km 1.000-m gauge (150 km electrified) (2006) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 98,721 km
paved: 80,280 km (includes 1,821 km of expressways) unpaved: 18,441 km (2004) |
|
Waterways:
|
7,200 km
note: Peninsular Malaysia 3,200 km; Sabah 1,500 km; Sarawak 2,500 km (2008) |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 306
by type: bulk carrier 12, cargo 97, carrier 1, chemical tanker 34, container 46, liquefied gas 33, passenger/cargo 5, petroleum tanker 71, roll on/roll off 3, vehicle carrier 4 foreign-owned: 40 (Germany 1, Hong Kong 14, Japan 4, Russia 2, Singapore 16, Sweden 3) registered in other countries: 68 (Bahamas 13, Marshall Islands 3, Norway 1, Panama 12, Philippines 1, Saint Kitts and Nevis 1, Singapore 27, Thailand 3, Tuvalu 1, US 2, unknown 4) (2008) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Bintulu, Johor Bahru, Kuantan, Labuan, George Town (Penang), Port Kelang, Tanjung Pelepas |
|
Transportation - note:
|
the International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the Strait of Malacca and South China Sea as high risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; numerous commercial vessels have been attacked and hijacked both at anchor and while underway; hijacked vessels are often disguised and cargo diverted to ports in East Asia; crews have been murdered or cast adrift |
| Military | Malaysia |
|
Military branches:
|
Malaysian Armed Forces (Angkatan Tentera Malaysia, ATM): Malaysian Army (Tentera Darat Malaysia), Royal Malaysian Navy (Tentera Laut Diraja Malaysia, TLDM), Royal Malaysian Air Force (Tentera Udara Diraja Malaysia, TUDM) (2009) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service (2005) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 6,440,338
females age 16-49: 6,280,826 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 5,493,946
females age 16-49: 5,409,524 (2009 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:
|
male: 266,267
female: 252,543 (2009 est.) |
|
Military expenditures:
|
2.03% of GDP (2005 est.) |
| Transnational Issues | Malaysia |
|
Disputes - international:
|
Malaysia has asserted sovereignty over the Spratly Islands together with China, Philippines, Taiwan, Vietnam, and possibly Brunei; while the 2002 "Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea" has eased tensions over the Spratly Islands, it is not the legally binding "code of conduct" sought by some parties; Malaysia was not party to the March 2005 joint accord among the national oil companies of China, the Philippines, and Vietnam on conducting marine seismic activities in the Spratly Islands; disputes continue over deliveries of fresh water to Singapore, Singapore's land reclamation, bridge construction, and maritime boundaries in the Johor and Singapore Straits; in November 2007, the ICJ will hold public hearings in response to the memorials and countermemorials filed by the parties in 2003 and 2005 over sovereignty of Pedra Branca Island/Pulau Batu Puteh, Middle Rocks and South Ledge; ICJ awarded Ligitan and Sipadan islands, also claimed by Indonesia and Philippines, to Malaysia but left maritime boundary and sovereignty of Unarang rock in the hydrocarbon-rich Celebes Sea in dispute; separatist violence in Thailand's predominantly Muslim southern provinces prompts measures to close and monitor border with Malaysia to stem terrorist activities; Philippines retains a dormant claim to Malaysia's Sabah State in northern Borneo; Brunei and Malaysia agreed in September 2008 to resolve their offshore and deepwater seabed dispute, resume hydrocarbon exploration and renounce any territorial claims on land; piracy remains a problem in the Malacca Strait |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): 15,174 (Indonesia); 21,544 (Burma) (2007) |
|
Trafficking in persons:
|
current situation: Malaysia is a destination and, to a lesser extent, a source and transit country for women and children trafficked for the purpose of commercial sexual exploitation, and men, women, and children for forced labor; Malaysia is mainly a destination country for men, women, and children who migrate willingly from South and Southeast Asia to work, some of whom are subjected to conditions of involuntary servitude by Malaysian employers in the domestic, agricultural, construction, plantation, and industrial sectors; to a lesser extent, some Malaysian women, primarily of Chinese ethnicity, are trafficked abroad for commercial sexual exploitation
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Malaysia improved from Tier 3 to the Tier 2 Watch List for 2008 when it enacted comprehensive anti-trafficking legislation in July 2007; however, it did not take action against exploitative employers or labor traffickers in 2007; the government has not ratified the 2000 UN TIP Protocol (2008) |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
drug trafficking prosecuted vigorously and carries severe penalties; heroin still primary drug of abuse, but synthetic drug demand remains strong; continued ecstasy and methamphetamine producer for domestic users and, to a lesser extent, the regional drug market |
|
This page was last updated on 14 May, 2009 |