








NOARCHIVELOG mode protects a database only from instance failure, not from disk (media) failure. Only the most recent changes made to the database, stored in the groups of the online redo log, are available for instance recovery. In other words, if you are using NOARCHIVELOG mode, you can only restore (not recover) the database to the point of the most recent full database backup. You cannot recover subsequent transactions.
Also, in NOARCHIVELOG mode, you cannot perform online tablespace backups. Furthermore, you cannot use online tablespace backups previously taken while the database operated in ARCHIVELOG mode. Only full backups taken while the database is closed can be used to restore a database operating in NOARCHIVELOG mode. Therefore, if you decide to operate a database in NOARCHIVELOG mode, take full database backups at regular, frequent intervals.
Figure 22 - 1 illustrate how the database's online redo log is generated by the process archiving the filled groups (ARCH in this illustration).
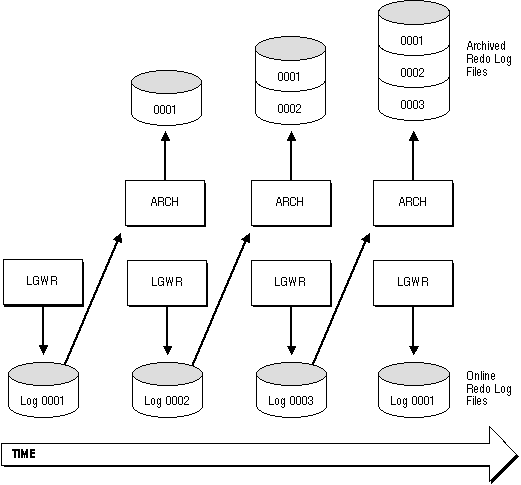
Figure 22 - 1. Online Redo Log File Use in ARCHIVELOG Mode
ARCHIVELOG mode enables complete recovery from disk failure as well as instance failure, because all changes made to the database are permanently saved in an archived redo log.
If all databases in a distributed database operate in ARCHIVELOG mode, you can perform coordinated distributed database recovery. However, if any database in a distributed database uses NOARCHIVELOG mode, recovery of a global distributed database (to make all databases consistent) is limited by the last full backup of any database operating in NOARCHIVELOG mode.
Also, the entire database can be open and available for normal use while you back up or recover all or part of the database in ARCHIVELOG mode. Note that extra administrative operations are required to manage the files of the archived redo log, and that you must have a dedicated tape drive or additional disk space to store the archived redo log files when the database operates in ARCHIVELOG mode.
You must also decide how filled groups of the online redo log are to be archived. An instance can be configured to have Oracle automatically archive filled online redo log files, or you can manually archive filled groups.
See Also: You can also configure Oracle to verify redo log blocks when they are archived. For more information, see "Verifying Blocks in Redo Log Files" ![[*]](jump.gif) .
.




